Data Mart
26 Jul 2023Empowering Targeted Insights and Decision-Making
In data management and analytics, organizations often face the challenge of efficiently accessing and analyzing vast amounts of data scattered across multiple sources. To address this issue, Data Marts have emerged as a powerful solution, providing targeted and specialized datasets tailored to specific business needs. In this article, we explore the concept of Data Marts, their key features, benefits, and their crucial role in driving data-driven decision-making.
Understanding Data Marts
A Data Mart is a small, focused, independent subset of an Enterprise Data Warehouse (EDW) that stores data relevant to a specific business function, department, or user group. Unlike an EDW’s comprehensive and centralized nature, Data Marts is designed to serve the unique requirements of particular business units, offering simplified and optimized access to relevant data.
Data Marts typically use a dimensional data model, such as star schema or snowflake schema, to organize data for analytical purposes. These models are highly optimized for querying and reporting, enabling faster data retrieval and analysis.
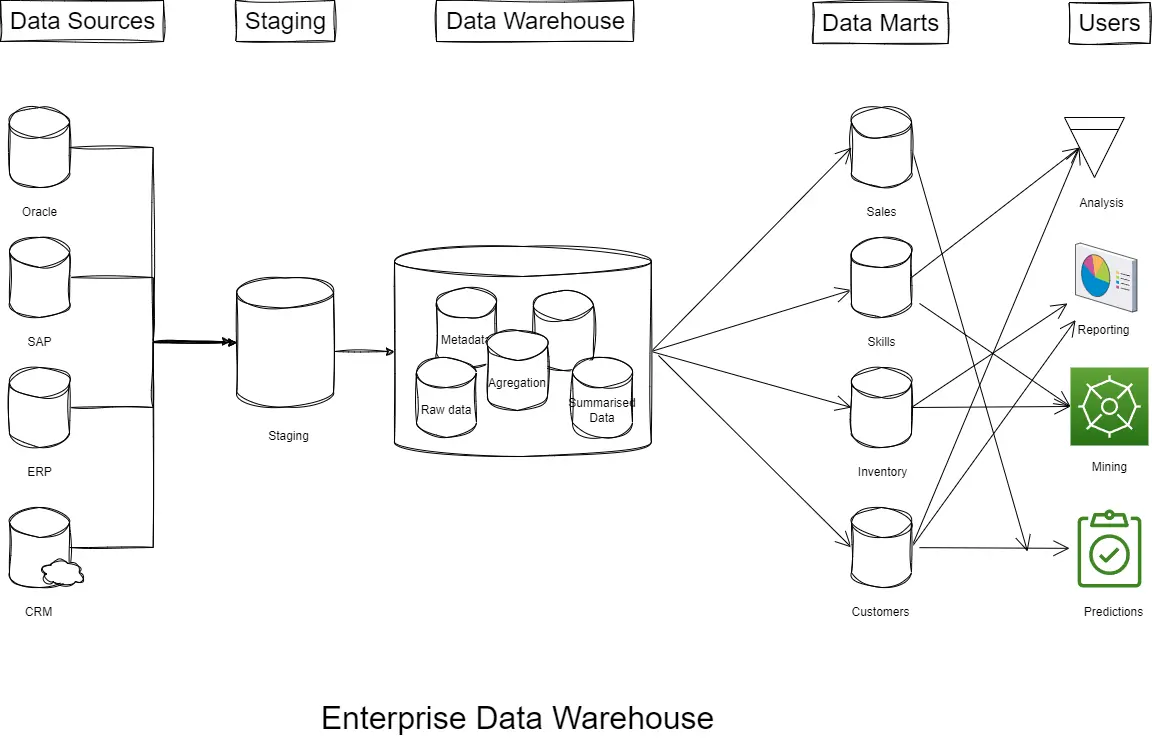
Key Features of Data Marts
-
Focused Data Scope: Data Marts are purpose-built for specific business needs, focusing on a particular department or functional area. This targeted approach ensures users can access the most relevant and meaningful data for their analytical tasks.
-
Data Simplification: Data Marts transform complex and extensive datasets into simplified structures, making it easier for business users to access and interpret the data. This simplification improves user adoption and enhances the decision-making process.
-
Improved Performance: Data Marts can significantly improve query performance and reduce data retrieval time by storing only relevant data. This speed is crucial for business users who require real-time or near-real-time insights.
-
Autonomous and Decentralized: Data Marts operate independently, allowing different departments to autonomously manage their datasets and reporting requirements. This decentralization promotes agility and flexibility in data management.
-
Customization: Data Marts can be customized to suit the specific needs of their business unit. Customization ensures that users get tailored insights aligned with their unique analytical needs.
Benefits of Data Marts
-
Business Agility: Data Marts enable organizations to respond quickly to changing business needs. With dedicated datasets for specific business units, decision-makers can swiftly access relevant data and make informed choices.
-
Enhanced Performance: The optimized structure of Data Marts translates to faster query performance and reduced latency. This boost in performance empowers users with timely insights for critical decision-making.
-
User Empowerment: Data Marts put the power of data analysis in the hands of business users. Users can perform self-service analytics without relying on IT teams by providing simplified and easy-to-understand data.
-
Reduced Impact on EDW: Data Marts offload analytical queries from the central EDW, reducing the load on the primary system and ensuring smooth and efficient operations for all users.
-
Cost-Effectiveness: By focusing on specific data needs, Data Marts can be implemented more cost-effectively than a comprehensive EDW. This makes data warehousing solutions more accessible to organizations with budget constraints.
Conclusion
Data Marts are pivotal in democratizing data and fostering data-driven decision-making within organizations. By providing targeted, user-friendly datasets, Data Marts empower business users to gain meaningful insights quickly and efficiently.
Incorporating Data Marts into a comprehensive data management strategy alongside an Enterprise Data Warehouse offers a powerful combination that addresses centralized and specialized analytical needs. As organizations continue to harness the power of data to drive success, Data Marts will remain a critical tool in the pursuit of optimized decision-making, improved performance, and enhanced business agility.