Multi Dimensional Database (MDDB)
26 Jul 2023Unleashing the Power of Analytical Insights
In data-driven decision-making, businesses rely on sophisticated tools and technologies to extract valuable insights from vast data. One such powerful tool is the Multi-Dimensional Database (MDDB), a specialized database optimized for analytical processing. In this article, we explore the concept of Multi-Dimensional Databases, their unique features, and advantages, and how they enable organizations to unlock the full potential of their data.
Understanding Multi-Dimensional Databases (MDDB)
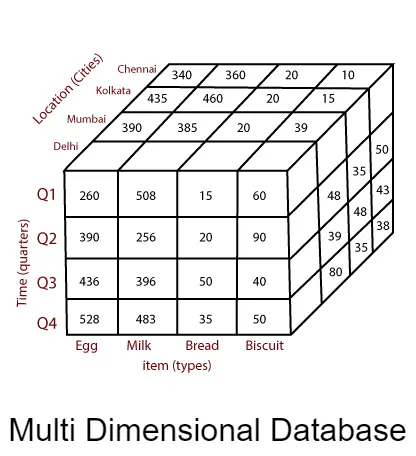
A Multi-Dimensional Database is a type of database specifically designed to handle and store multi-dimensional data efficiently. It is highly optimized for analytical queries, enabling users to explore data from multiple perspectives or dimensions. Unlike traditional relational databases, which store data in tables with rows and columns, MDDBs utilize a multi-dimensional model to organize data along multiple axes.
The multi-dimensional model represents data in a cube-like structure, where each axis corresponds to a specific dimension. For example, in sales data, dimensions could include time, products, regions, and sales representatives. Each cell in the cube holds a data point, such as sales revenue, which can be analyzed along various combinations of dimensions.
Key Features of Multi-Dimensional Databases
-
Multi-Dimensional Data Model: The essence of MDDB lies in its multi-dimensional data model, which allows users to analyze data across multiple dimensions simultaneously. This structure enhances the speed and flexibility of data analysis.
-
Fast Query Performance: MDDBs are designed for quick query performance, making them ideal for complex analytical queries that involve aggregations, calculations, and slicing and dicing of data.
-
Aggregation Support: MDDBs can efficiently pre-aggregate data, reducing the need for recalculating values during query execution. This feature speeds up query response times, even with large datasets.
-
OLAP (Online Analytical Processing) Compatibility: MDDBs are well-suited for OLAP applications that involve multi-dimensional analysis, data mining, and ad-hoc querying.
-
Dimensional Hierarchies: MDDBs support hierarchical relationships between dimensions, allowing users to drill down or roll up data to various levels of granularity.
Advantages of Multi-Dimensional Databases
-
Rapid Decision-Making: The fast query performance of MDDBs enables users to obtain real-time insights quickly. Business leaders can make informed decisions promptly, reacting to changing market conditions and opportunities.
-
Complex Data Analysis: MDDBs excel at complex analytical tasks, such as trend analysis, forecasting, and what-if scenarios. Users can perform advanced analytics without the need for extensive programming skills.
-
User-Friendly Interfaces: MDDBs often have intuitive user interfaces that facilitate self-service analytics. Non-technical users can explore data and generate reports without relying on IT support.
-
Reduced Data Redundancy: By storing data in a compact, multi-dimensional format, MDDBs reduce data redundancy and storage requirements, optimizing resource utilization.
-
Enhanced Data Visualization: Multi-dimensional data lends itself well to data visualization techniques, making it easier for users to grasp complex relationships and patterns.
Conclusion
The Multi-Dimensional Database is a powerful tool revolutionizing how organizations process and analyze data. With its ability to handle complex multi-dimensional data models, fast query performance, and support for sophisticated analytics, MDDBs empower businesses to gain deeper insights into their operations, customers, and markets.
By leveraging the capabilities of Multi-Dimensional Databases, companies can uncover valuable patterns, trends, and correlations that were once hidden within their data. In the rapidly evolving business landscape, the ability to make data-driven decisions quickly and accurately can be a significant competitive advantage. As organizations continue to harness the power of data, Multi-Dimensional Databases will remain at the forefront of enabling analytical excellence and propelling businesses toward success.